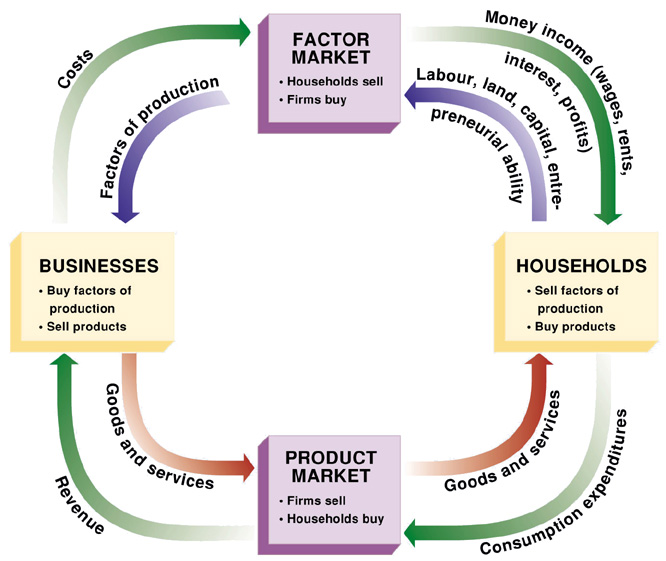
Circular Flow Diagram
It represents the transaction in the economy.
- Resource (Product) Market: this is the place where households sell resources and businesses buy resources. (Goods & services)
- Factor Market: holds your factors of production.
- Firm: an organization that provides goods and services for sale. Firms sell finished products to households.
- Household: a person or group of people that share their income. Household sell their factors of production to businesses.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The market value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders within a given year.
- Gross national Product (GNP): the total value of all final goods and services by citizens of that country on its land or foreign land.
- What's included in GDP
- C - Personal consumption expenditures
- Ig - Gross Private Domestic Investment
- Factory equipment
- Factory equipment maintenance
- Construction of housing
- Unsold inventory of products built in a year
- G - Government spending
- Xn - Net exports (exports-imports)
- What's not included in GDP
- Intermediate goods: goods that required further processing before they're ready for final use.
- Used/Secondhand goods
- Avoid double counting
- Purely financial transaction (stocks and bonds)
- Illegal activities (drugs)
- Unreported business activity (unreported tips)
- Transfer Payments
- Public (social security, welfare)
- Private (scholarship)
- Non-market activity
- Volunteer work
- Babysitting
- Any work you performed yourself
2 Ways of Calculating GDP
- Expenditure approach: add up all of the spending on final goods and services produced in a year.
GDP = C + Ig + G + Xn - Income approach: add up all of the income that resulted from selling all final goods and services produced in a given year. Rarely used because people lie about their income.
GDP = W + R + I + P + Statistical adjustment - Compensation of Employees: include wages, salaries, social security contribution, and health and pension plans.
- Rents: income of property owners.
- Interest: income that comes from money.
- Corporate profits: the income of the company stockholders.
- Proprieter's income: the income of sole proprietorship and incomeship.
- Statistical adjustment
- Indirect business taxes
- Depreciation
- Net foreign factor payment
Formulas
- Budget: government purchases of goods and services + government transfer payments - government tax and fee collection
Positive # = Budget Deficit Negative # = Budget Surplus - Trade: exports - imports
Positive # = Trade Surplus Negative # = Trade Deficit - National income:
- compensation of employees + rental income + interest income + corporate profits + proprietor's income
- GDP - indirect business taxes - depreciation - net foreign factor payment
- Disposable Personal Income: national income - personal household taxes + government transfer payments
- GNP = GDP + Net foreign factor payment
- Net Domestic Product (NDP): GDP - depreciation
- Net National Product (NNP): GNP - depreciation
- Real GDP: the value of output produced in constant base year prices. Increase only if quantity increases. Used to measure economic growth. Price X Quantity
- Nominal GDP: the value of output produced in current prices. It can increase from year to year if price and quantity increase. Used to measure price increases (inflation). Price X Quantity
- GDP Deflator: a price index used to adjust from nominal to real GDP.
(Nominal GDP / Real GDP) X 100 - Consumer Price Index (CPI): the most commonly used measurement of inflation for consumers.
(Current year / Base year) X 100 - Calculation for inflation: (GDP Deflator of current year - GDP Deflator of base year) / Base year X 100
- In the base year GDP Deflator is 100.
- For years after the base year, GDP Deflator is greater than 100.
- For years before the base year, GDP Deflator is less than 100.
Real Interest Rate vs. Nominal Interest Rate
- Real interest rate was adjusted for inflation
- Nominal interest rate was not adjusted for inflation
- Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation
Inflation
It taxes those who receive relatively fixed income.
Unanticipated Inflation
- Hurt by Inflation
- Lenders
- People with a fixed income (elderly, welfare)
- Savers
- Helped by Inflation
- Debtors
- A business where the price of the product increases faster than the price of resources.
- COLA: Cost of Living Adjustment
Unemployment
The failure to use available resources particularly labor to produce desired goods and services.
- Unemployment Rate: 4% to 5% = Full employment or Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
- Labor Force:
- Above 16 years of age
- Able and willing to work
- Not in the Labor Force:
- Military
- Jail/Prison
- Mental Institutions
- Retired people
- Students
- Homemaker
- People who are not looking for a job
- How to calculate the unemployment rate: # of unemployed / (# of employed + # of unemployed) X 100
- Type of Unemployment:
- Frictional: temporarily unemployed or in between jobs.
- High school or college graduate looking for an opportunity
- Better position
- Structural: workers do not have transferable skills and these jobs never come back.
- Seasonal: type of unemployment due to the time of the year and nature of job.
- Cyclical: results from economic downturns. As demands for goods and services fall, demand for labor and worker also fall.
GDP Gap
The amount by which actual GDP falls short of potential GDP.
- Okun's Law: states for every 1% that actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate of unemployment. A GDP gap of about 2% occurs.
- Rule of 70: it is used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double given a particular annual growth rate.
70 / (Interest rate)